|
|
Using the Solver Function
From NeoWiki
| Revision as of 16:24, 14 April 2007 (edit) Lorinda (Talk | contribs) (Polished "Problem Presentation") ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 14:35, 15 April 2007 (edit) (undo) Jgd (Talk | contribs) (add link to wiki openoffice Optimization Solver. Change titles level) Next diff → |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| The '''Solver''' in Calc is a tool that helps you to calculate the conditions which maximize profit and minimize cost while satisfying some constraints. It can solve linear or non-linear problems, but keep in mind that the non-linear problems are much more difficult to solve. The example below shows the utilisation of the '''Solver''' function in Calc.<br> | The '''Solver''' in Calc is a tool that helps you to calculate the conditions which maximize profit and minimize cost while satisfying some constraints. It can solve linear or non-linear problems, but keep in mind that the non-linear problems are much more difficult to solve. The example below shows the utilisation of the '''Solver''' function in Calc.<br> | ||
| - | + | ==Problem Presentation== | |
| Let us assume that a factory produces three types of machines, A1, A2, A3. Let ''pi'' be the cost of the raw material and ''hi'' the number of hours which are necessary to produce a machine of the type Ai. The profit per machine of the type Ai is equal to ''bi''.<br> | Let us assume that a factory produces three types of machines, A1, A2, A3. Let ''pi'' be the cost of the raw material and ''hi'' the number of hours which are necessary to produce a machine of the type Ai. The profit per machine of the type Ai is equal to ''bi''.<br> | ||
| The decision variables are the numbers ''xi'' of machines of the type Ai which are produced. | The decision variables are the numbers ''xi'' of machines of the type Ai which are produced. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ==Solving the Problem== | ||
| * Open a Calc document | * Open a Calc document | ||
| Line 84: | Line 85: | ||
| * You can save that model by clicking the {{button|Save}} button. By clicking the {{button|Load}} button, you will be able to display it later and, for instance, to modify the values of the constraints or of the production costs. | * You can save that model by clicking the {{button|Save}} button. By clicking the {{button|Load}} button, you will be able to display it later and, for instance, to modify the values of the constraints or of the production costs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Link== | ||
| + | [[http://wiki.services.openoffice.org/wiki/Optimization_Solver#User_Interface Solver Descripition]] | ||
| {{botlangbarEN|[[Fr:Utiliser le Solver|Français]] [[It:Utilizzare_la_Funzione_Solver|Italiano]]}} | {{botlangbarEN|[[Fr:Utiliser le Solver|Français]] [[It:Utilizzare_la_Funzione_Solver|Italiano]]}} | ||
| [[Category:Tips and Hints]][[Category:NeoOffice]] | [[Category:Tips and Hints]][[Category:NeoOffice]] | ||
Revision as of 14:35, 15 April 2007
The Solver in Calc is a tool that helps you to calculate the conditions which maximize profit and minimize cost while satisfying some constraints. It can solve linear or non-linear problems, but keep in mind that the non-linear problems are much more difficult to solve. The example below shows the utilisation of the Solver function in Calc.
Problem Presentation
Let us assume that a factory produces three types of machines, A1, A2, A3. Let pi be the cost of the raw material and hi the number of hours which are necessary to produce a machine of the type Ai. The profit per machine of the type Ai is equal to bi.
The decision variables are the numbers xi of machines of the type Ai which are produced.
We want to calculate the values of the numbers xi which minimize the total profit.
These data have to satisfy some constraints, for example:
- every number xi must be an integer. We want to produce at least 30 machines of each type.
- the total cost of raw material must be less than or equal to $10,000
- the total number of working hours must be less than or equal to 5,200.
| Machines | A1 | A2 | A3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of machines | x1 | x2 | x3 |
| Cost of raw material per machine | p1 | p2 | p3 |
| Number of working hours per machine | h1 | h2 | h3 |
| Profit per machine | b1 | b2 | b3 |
| Profit to maximize | b1x1+b2x2+b3x3 | ||
| Constraints | x1 >= 30, x2 >= 30, x3 >= 30 | p1x1+p2x2+p3x3 <= 10 000 | h1x1+h2x2+h3x3 <= 5 200 |
Solving the Problem
- Open a Calc document
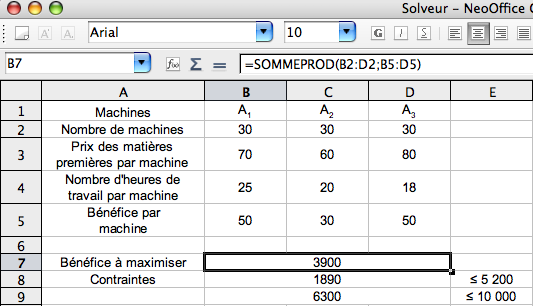
- In the spreadsheet, enter the data as in the table below:
The value 1890 contained in the cell B8 is the sum of working hours necessary to produce 30 machines of each type, namely SOMMEPROD(B2:D2;B4:D4).
The value 6300 contained in the cell B9 is the cost of raw material necessary to produce 30 machines of each type, namely SOMMEPROD(B2:D2;B3:D3).
We have to maximize the total profit: SOMMEPROD(B2:D2;B5:D5)
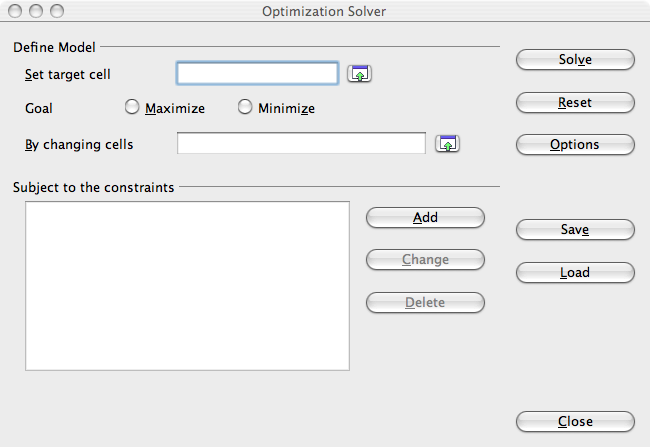
- Choose the Outils > Solver… menu. The Optimization Solver window appears.
- Define the model:
N.B All the references are automatically translated into absolute references by the solver. That explains the presence of the prefix "$" in the cells adresses.
- Click on the little green arrow to the right of the Set target cell field, then click on the cell which contains the measure to optimize, here B7 which contains the formula giving the total profit. Click on the arrow to the right of the input field again, the value $Sheet1.$B$7 is automatically placed in the Set target cell field.
- Click on Maximize. It's the goal to assignate.
- Click on the little green arrow to the right of the Set target cell field, in order to choose the cells containing the decision variables whose values allowing the profit maximization have to be computed. Select the three cells B2, C2, D2 by dragging the mouse. Click on the arrow to the right of the input field again. The range $Sheet1.$B$2:$D$2 is automatically placed in the By changing cells field.
- Define the constraints:
Let us set the following constraints:
- SOMMEPROD(B2:D2;B4:D4) ≤ 5 200
- SOMMEPROD(B2:D2;B3:D3) ≤ 10 000
- B2 ≥ 30
- C2 ≥ 30
- D2 ≥ 30
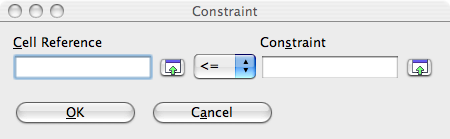
- Click the Add button. The Constraint window appears.
- Click on the little green arrow to the right of the Cell reference field and click on the cell B8, then on the arrow again.
- In the Constraint field enter the value you desire, namely 5200.
- Click OK.
- Click on the Add button again and add the four other constraints in the same way. Change the sign "<=" into ">=" for the constraints that are imposed on the values xi.
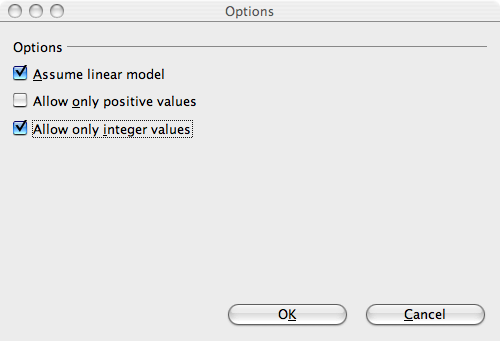
- Choose the options :
- Click on the Options button
- In the Options window that appears, leave the default option Assume linear model checked and check the Allow only integer values option.
- Click OK.
- Click on the Solve button.
- The message Solution found appears in a dialog box. Click OK.
The values of cells B2 to D2 have been changed so that the profit may be maximum, under the conditions set by the constraints.
In that example we get x1= 82, x2 = 31 et x3 = 30.
- You can save that model by clicking the Save button. By clicking the Load button, you will be able to display it later and, for instance, to modify the values of the constraints or of the production costs.
Link